
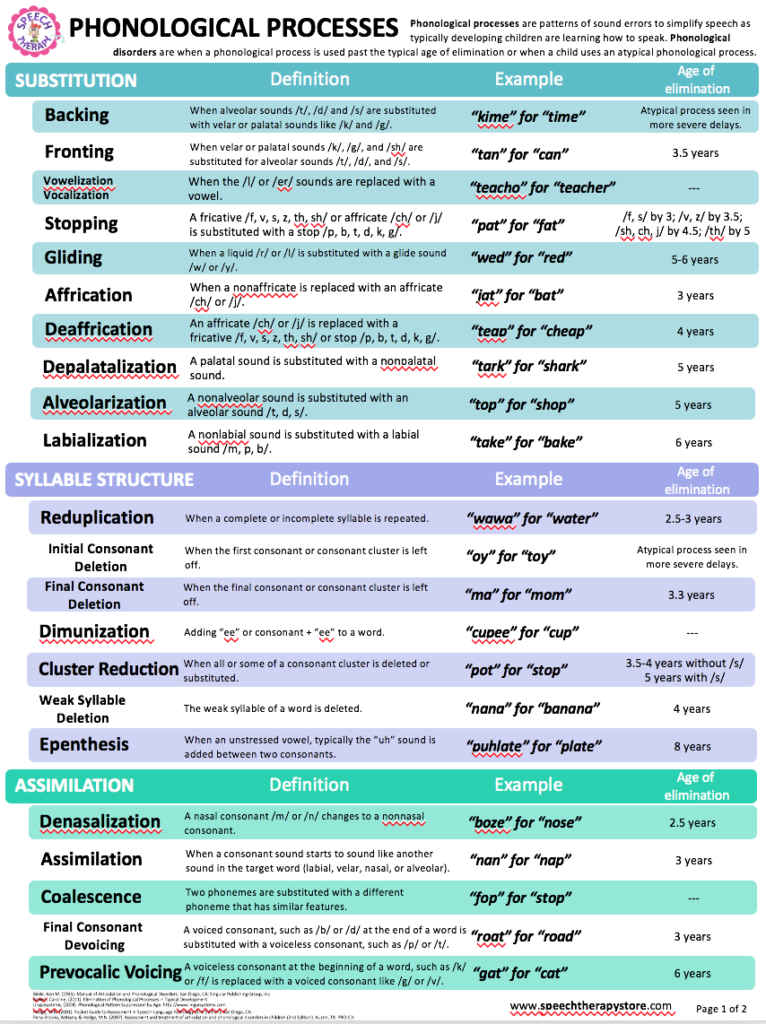
For example, although ‘fronting’ is a typical process, ‘backing’ is not. The more severe a child’s speech disorder, the longer treatment will take.Ĭhildren with more severe phonological disorders may exhibit ‘atypical phonological processes’ – error patterns that are not produced in typically developing children. Judgments of severity are based on the number of error processes the child exhibits, their overall speech intelligibility, and how typical or atypical their errors are. Phonological errors usually involve substitutions (e.g., (‘cup’ to “tup”) or omissions (e.g., ‘star’ to “tar”).Ĭhildren with phonological disorder may range from mild to severe. For example, velar fronting is typically suppressed by age 3½, so a child who is fronting at age 5 is considered to have a phonological delay.

Most often, these errors are those younger children make (‘phonological processes’), but the child did not suppress them at the age children typically do. For example, they may exhibit ‘velar fronting’ in which they substitute /k/ and /g/ with /t/ and /d/ (‘cup’ to “tup”, ‘go’ to “doh”). For example, we know that in the words ‘cat’ and ‘pat’ they differ by one phoneme (/k/ and /p/) and that this changes the word’s meaning.Ĭhildren with phonological disorders typically make predictable, rule-based speech errors. This system is how our brains represents how speech sounds influence meaning. Children with phonological disorder may have a family history of the same, but this is not always the case.Ĭhildren with a phonological speech disorder have phonological systems that are not developing as expected. Phonological disorder is a type of speech sound disorder.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
